Probably, one of the best SEO advice you have been hearing for a while now is “Optimize for the users.”
I do not want to belittle this advice and truly believe in its value. But, before implementing this advice, you must make your site technically apt for Google. And here is where technical SEO comes into the picture.
So, when did you last scrutinize your technical SEO status? Maybe a long time back. So, here are the 12 most common and inevitably damaging technical SEO errors you must fix ASAP.
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to optimizing a site and server so the search engine can seamlessly crawl and index the site. It includes optimizing the site architecture and other technical factors for better online visibility.
Unlike page optimization, technical SEO generally refers to site-wide changes. Technical
SEO comprehensively covers JavaScript indexing, SEO tags implementation, Sitemaps, Meta tags, links, keywords, etc.
Here you need to fix several site-wide factors to meet the technical requirements of search engines. Thus, helping the site to index and render appropriately and rank in the SERPs.
Here is the List of the Most Common Technical SEO Issues:
- An Issue with Site Indexation
So, you switched to Google to check your site rankings but failed to find your listing. You even tried to search with your brand name, but with no gain.
There might be an issue with your site indexation.
So, unless your site is indexed appropriately, it has no existence for search engines.
To check if your site has some indexation issue, you can Google “site:yoursitename.com”
The results will show you all the indexed pages of your site.
Now, You Can Analyze And Fix Some Of The Common Indexation Issues:
- You must manually initiate indexing if you see no listings from your domain. Here is what you need to check.
- If you can’t find some site pages in the list of indexed pages, you need to check these pages. Ensure they abide by Google’s Webmaster Guidelines, or there can be some optimization issues.
- If some important site pages aren’t showing in listings, check the Robots.txt file. You might have blocked these pages in the Robots.txt file. Sometimes, you might have forgotten to remove the NOINDEX tags from these pages.
- If you see more pages than expected, these can be due to two cases. Either you have some old site pages still ranking, or your site has fallen victim to hacking spam.
- If some pages from the older site version rank, you need to redirect them to new ones.
- In hacking spam, create a list of spam pages and use Google’s Disavow Tool to remove them.
- Robots.txt File Isn’t Compiled Appropriately.
You probably know that you cannot miss out on adding the Robots.txt file to your site. But, what else that can mess up your technical SEO is an incorrect Robots.txt file.
The mistakes in your Robots.txt file are generally made by a developer while rebuilding your site.
How Can You Check If Your Robots.Txt File Isn’t Configured Correctly?
Type “yoursitename.com/robots.txt” in the Google search bar. If the result shows “User-agent:*Disallow:/,” you must rectify the Robots.txt file.
This error prevents all search engine robots from crawling your site pages.
Here is how the error looks:

How To Fix The Poorly Configured Robots.Txt File?
- The “Disallow:/” error is something your developer needs to fix asap. He might have an explanation for this configuration or might have carelessly missed it.
- If you have an e-commerce website, you will likely have a complex Robots.txt file. Here you would need to scrutinize the Robots.txt file line by line along with the developer.
- The NOINDEX Tag Isn’t Removed.
The NOINDEX tag tells Google not to index your webpage. The tag will remove a page’s existence from Google’s index altogether.
A developer adds the NOINDEX tag while the site is in production. And he has to remove the tag while making the site live.
However, in many cases, a developer forgets to remove the NOINDEX tag.
You can do a manual check by checking the page’s source code for “NOINDEX” tags.
However, a better way is to use the Screaming Frog tool to scan all site pages at once.
If you find these tags, you can change them to “INDEX” tags or remove the NOINDEX tag.
Things to implement:
- If your site undergoes constant modification, developers must be extra careful about removing NOINDEX tags.
- You must ensure you check your site every week during the constant upgrades.
- Your Site Doesn’t have an XML Sitemap.
Search engine crawlers can index your site if you have a well-defined internal link structure.
However, the XML sitemap guides the crawlers to comprehend your site structure. Thus, helping crawlers choose the most efficient way to index your site.
You can use online tools to generate sitemaps.
It also ensures that all your optimized site pages are indexed properly. It is quite crucial for complex sites with hundreds to thousands of pages.
You may find one of these XML sitemap issues:
- The site lacks a sitemap;
- The location of the sitemap isn’t mentioned in Robots.txt;
- You have not updated the sitemap after upgrading the site architecture;
- You have multiple sitemap copies on your site;
- You have most likely forgotten to remove the old sitemap copy while adding the new one.
How To Resolve The XML Sitemap Issue?
Check for all the above issues and resolve them with assistance from a developer.
If your site lacks an XML sitemap, prepare one with the help of a developer. You can also use Yoast Plugin or AIO SEO plugins for WordPress sites to generate sitemaps.
Also, examine the indexation of the pages you add to your XML sitemap. You can use Google Search Console for the same.
- Missing Canonical Tag
The rel=canonical tag is crucial when you have similar content sections on more than one page.
It is more common for e-commerce sites. When a product falls under multiple categories, Google considers these category pages duplicates.
The same issue strikes when a blog page falls under multiple categories.
Therefore, using the rel=canonical tag helps you point to the original page. Now Google crawlers can prioritize the original page and index it.
How To Check And Fix The Rel=Canonical Tag?
- You must spot-check the important pages of your site for the rel=canonical tag.
- A site audit tool will help you scan and reveal duplicate page errors. You can ask the developer to add the canonical tag on these pages.
- Improper 301 and 302 Redirection
Redirection is a crucial way to manage the dead pages and pass the link equity to important pages.
Redirects facilitate a hassle-free site migration and site upgrade process. And if you fail to use these redirects appropriately, you lose your traffic, rankings, and site authority.
That said, one must know how to employ 301 and 302 redirects.
301 is a permanent redirect and passes the highest link equity. And 302 is a temporary redirect that passes a comparatively lower share of link equity.
Some common misconceptions that you must be wary of:
- You can easily redirect all the 404 errors on your site. No, you cannot go redirect-crazy.
- You must redirect all URLs to the homepage to increase its authority. No, this can do more harm than good.
- Create more redirects to gain more link equity. No, this will ruin your site authority; you must keep your redirect list to a minimum.
- The rel=canonical tag will waste the link equity instead of redirecting to the original page. No, one can only do it in some cases.
How To Fix Redirection Errors?
- Check all your site URLs and the 404 errors. Redirect pages that either gain traffic or receives a link.
- Ask your SEO partner to check the 301 and 302 redirects. If there is a 302 redirect used for permanent redirection, change it to 301 redirects.
- Check the redirects that you implemented in the previous migration or re-launching process.
- Monitor the redirection report monthly or whenever you update your site.
- Broken Links Affecting Site Ranking
Many links break when you migrate or re-launch a site with new pages and URLs. Old pages may cease to exist, and the backlinks to these pages now read 404 errors. This causes you to lose your link equity.
You can use online tools to find broken links.
Moreover, many internal links too still point to the old pages. Thus, affecting the user experience significantly. It may also lead to the formation of some orphan pages.
How Can You Find This Issue?
Neil Rollins of Haitna says, “Use tools like Google Search Console and SEMrush to find your broken backlinks report. Google Search Console enables you to check the list of 404 errors. Here the broken backlink errors top the list”.
How To Resolve The Broken Links Errors?
Once you have a list of these 404 pages, 301 redirects them to the relevant new pages.
You can also contact some site owners to change the backlinks to your new page URL.
Use Google Alert and Mention tools to check which sites have mentioned your brand. You can ask them to give you backlinks to your new relevant pages.
Also, monitor your internal links each time there are significant content changes on the site.
- HTTP or “Not Secure” Site
HTTPS site security is no more an option. It affects your SEO and conversion rate optimization (CRO).
What’s worse is that when you enter an HTTP URL in Chrome:
- It shows the site URL in a grey background if it isn’t transactional.
- Or it shows a red highlighted “Not Secure” warning if the site has a transactional nature.
The “Not Secure” warning is most likely to off-put visitors, and they will bounce back.
You can use online tools to check for proper installation of SSL.
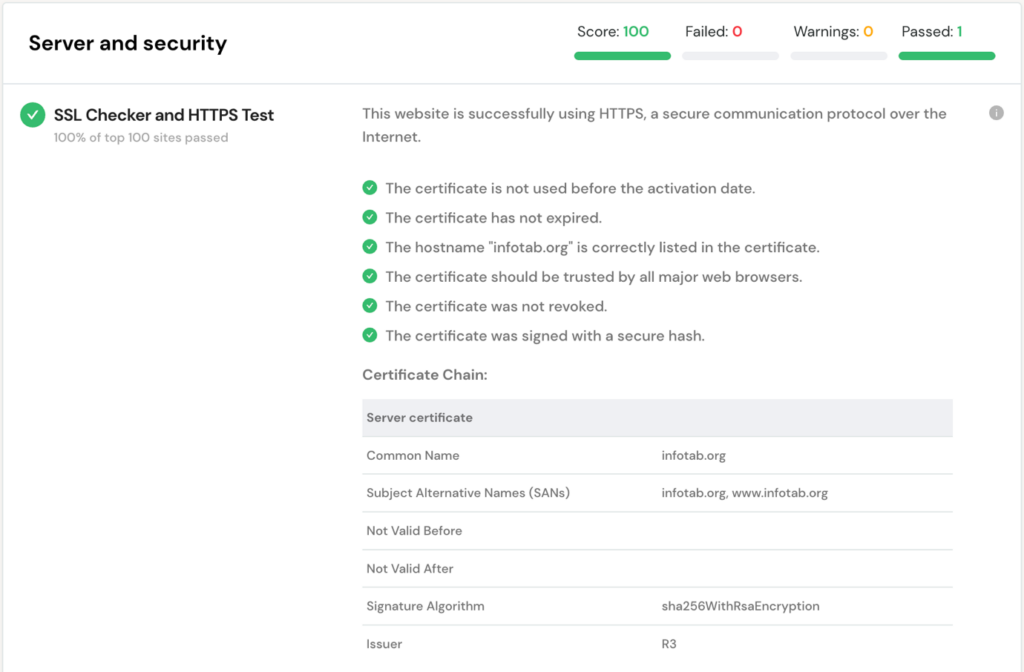
On the other end, the sites with HTTPS security are highlighted as “Secure” in Chrome.
So, you must consider buying the SSL security certificate for your site to make it HTTPS. You would then upload the certificate and migrate the site from HTTP to HTTPS.
Ensure that you do the migration work under an SEO expert’s supervision. He further makes sure that you do not lose any current SEO value.
- Slow Page Load Speed
A slow-loading website isn’t likely to impress Google or visitors. It messes with your site’s SEO power and conversion rate optimization (CRO).
Dotcom-Monitor reports that the bounce rate increases by 75% if a site takes more than 3 seconds to load.
Google recommends that the page load speed must not exceed 3 seconds for both desktop and mobile platforms.
And it expects e-commerce sites to load even faster. As Maile Ohye says in the Google Webmaster video:
She says, “2 seconds is the threshold for eCommerce website acceptability. At Google, we aim for under a half-second.”
Moreover, Google recently introduced the Page Experience Update in 2021. The update made Core Web Vitals one of the important ranking factors.
This update has made page speed all the more crucial for better SEO performance.
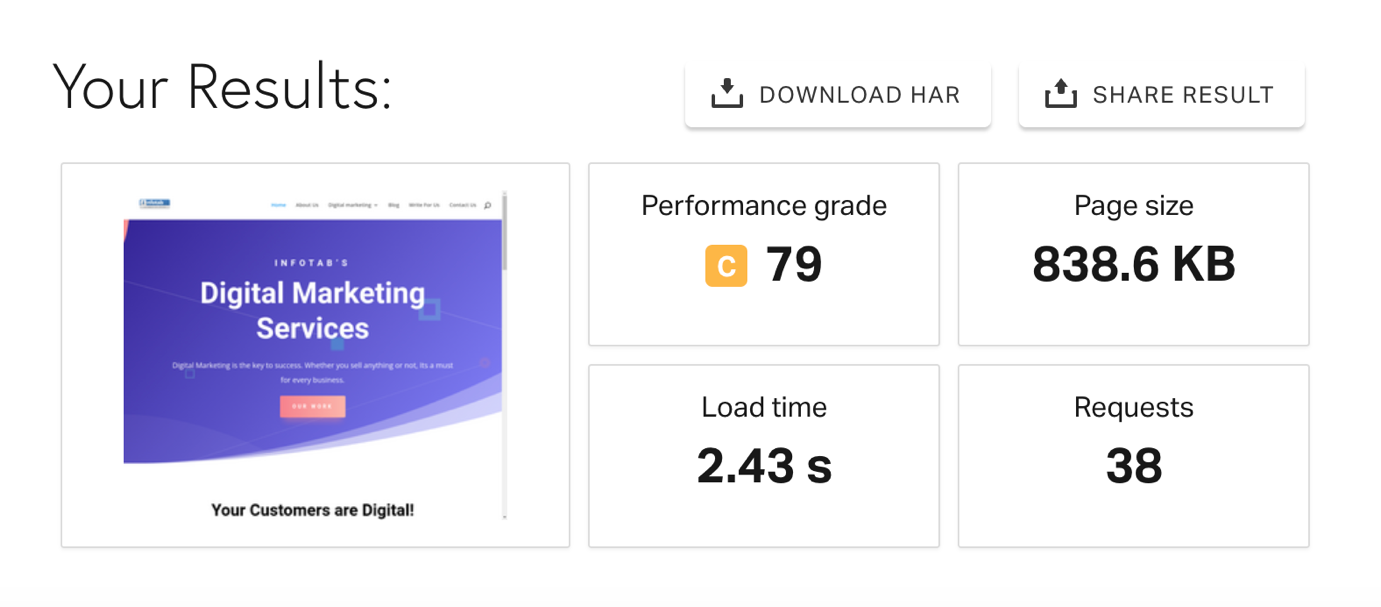
You can assess your website loading speed using the Google PageSpeed Insight tool. Ensure that you check for both the desktop and mobile versions.
The tool displays several errors and recommendations that you can follow for optimization.
See how we have optimized our website to load in less than 3 seconds.
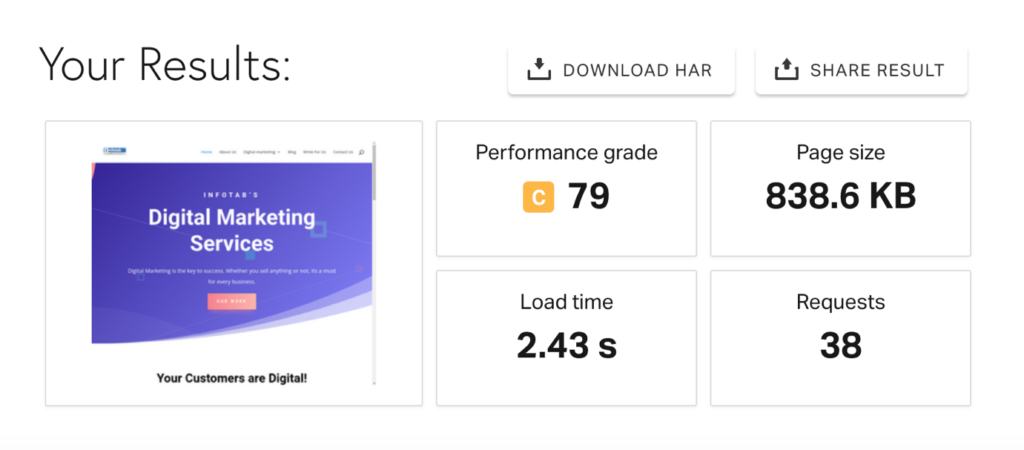
How To Resolve The Page Speed Issue For A Slow Site?
Some of the effective ways to optimize a site’s loading speed include:
- Employ content delivery network (CDN);
- Minify HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files;
- Use asynchronous loading;
- Gzip your WordPress files;
- Defer loading JavaScript files;
You can employ these optimization factors with the help of a developer.
- Unsynchronized Internal Linking Structure
A majority of webmasters do not prioritize internal linking. And an unsynchronized internal linking structure impacts your site’s crawlability.
It influences the way crawlers and users navigate through your site.
You must follow scalable internal linking if you have a multiple-page, complex site. A complex site without a defined structure will likely face indexation errors. And it might also produce orphan pages.
Another common issue is over-optimized anchor texts. Over-optimization can impact the quality of your on-page content.
The right internal linking structure helps share the link equity among the important pages. And it pushes your position higher in the SERPs.
How To Check And Fix The Internal Linking Structure?
- Conduct a technical audit of the site to check the internal link count. Check if the most crucial pages on your site are receiving adequate links. Also, check if there are any orphan pages.
- Take a manual look at all the in-content links across the site. See if there are any broken links, over-optimized anchor texts, or linking opportunities. Fix these errors.
- Ensure that your content creators follow a smart linking pattern whenever they post new content.
- Meta Tags Aren’t Optimized
Meta Tags have a considerable impact on your site’s SEO. They form your page’s preview snippet in the SERP listings. And your Meta Title or SEO Title is a valuable ranking factor.
But, often, businesses fail to optimize their Meta Tags and miss out on the meta description.
Your meta description has little to no impact on your SEO but is crucial for your page CTR.
As per best practices, you must add Meta Tags to all your indexed site pages.
The length of the Meta Title must not exceed 55 characters. And you must add the primary page keyword to the Meta Title.
The length of the meta description must not exceed 160 characters. Moreover, it must include important page keywords to boost relevancy.
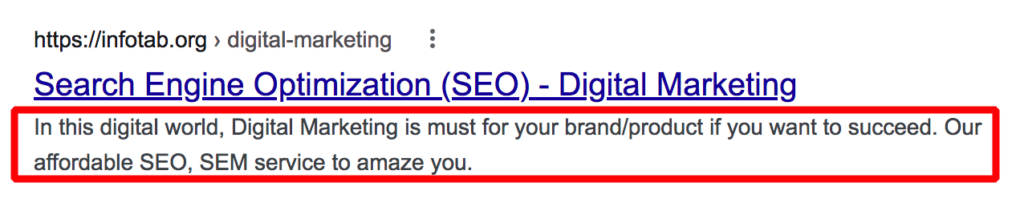
Check and resolve
You must check your Meta Tags status during the site’s SEO audit.
Look for the pages missing Meta Title or Meta Descriptions. Add the missing Meta Tags to all the important site pages.
Ensure that you do not miss out on the Meta Tags whenever you add a new page to the site.
- Site Images Aren’t Optimized and Lack Alt Tags.
Images are essential to construct the right user experience for your site. But, if you fail to optimize your images, they slow down your site.
Moreover, another common issue is the missing Alt tags. Alt tags are image description tags that define an image’s content for the crawlers.
The Alt tags must also include relevant page keywords to get some SEO advantage. This practice helps the images rank for image search in Google.

What’s The Way To Fix These Issues?
- When you run a speed test on your site, you get a list of image size errors. If you haven’t compressed your site images, you can use several tools to do the same. WPSmushit is one tool that helps you with image compression for WordPress sites.
- A site audit report can help you reveal the broken images and missing Alt tags. You can replace the broken images with optimized images. Also, ensure to add Alt tags to all the images on your site.
Technical SEO FAQs
Q1. How Crucial is Technical SEO for My Website?
Technical SEO is inevitably the first SEO implication you make on your website. It includes optimizing a site to match it with the technical requirements of search engines.
The search engine crawlers can now crawl and index your site seamlessly. Thus, helping it rank in the search engine page results.
Q2. Could You Suggest Me Some Technical SEO Fundamentals?
Here are the top technical SEO best practices you must implement:
- Scrutinize and optimize the Robots.txt file
- Add an XML sitemap to your site
- Check the rel=canonical tag and clarify the preferred URL
- Switch from HTTP to HTTPS
- Prepare a correct AMP Configuration
- Optimize site loading speed
- Check site indexation and resolve issues
- Make proper use of 301 and 302 redirects
- Fix broken backlinks and optimize internal linking
- Ensure that the developer removes NOINDEX tags before making the site live
- Optimize for mobile-first indexing
- Add and optimize Meta Tags and Alt Tags
Q3. Do You Need On-page SEO after Implementing Technical SEO?
Yes, you need on-page SEO to build over your technical SEO implementations. Except for the technical aspect, on-page SEO considers the content and UX of the site.
Some key on-page SEO considerations include:
- Optimizing the on-page content for the E-A-T ranking factor
- Choosing the right URL structure
- Optimizing the Meta Title and Meta Description
- Implementing the right header tags and relevant page headline
- Integration of Google Search Console and Google Analytics
Q4. Should I Ask My Developer to Do the Technical Optimization for Me?
You need to have a well-defined technical SEO strategy in place. You might need to do the site audits, SEO audits, etc., and prepare a list of areas that need optimization.
A seasoned SEO expert is a right person to help you implement technical SEO. Even if you do it yourself, you need to know all the know-how of it. A developer can only assist you with the implementations in the source code.
For example:
He can help you check the robots.txt file, implement redirects, optimize site speed, check mobile compatibility, etc. You need to strategize and manage all these SEO tasks.






